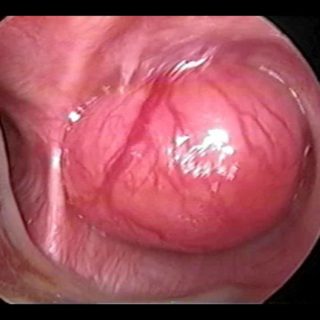
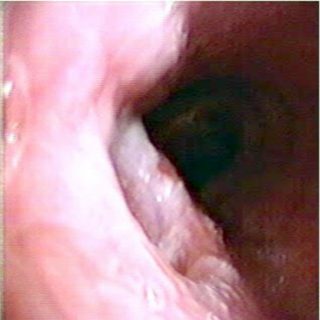
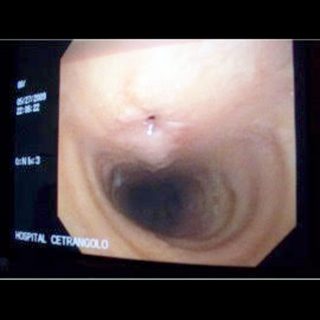
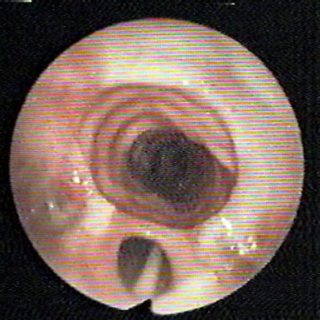
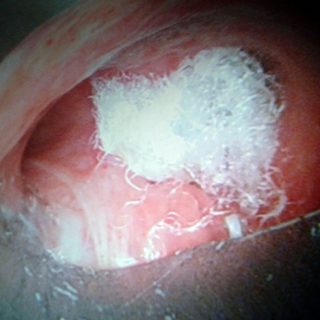
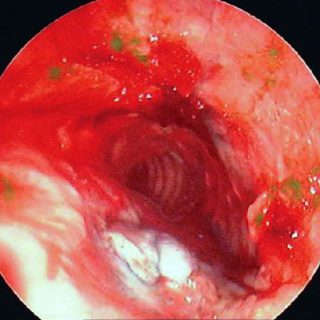
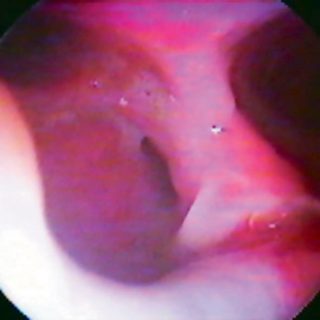
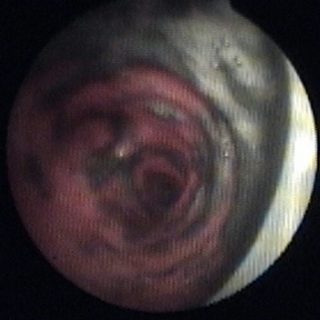
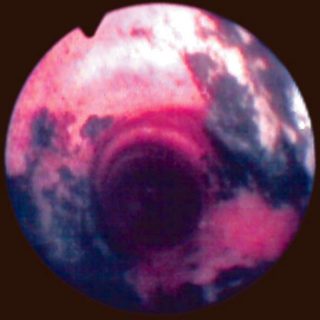
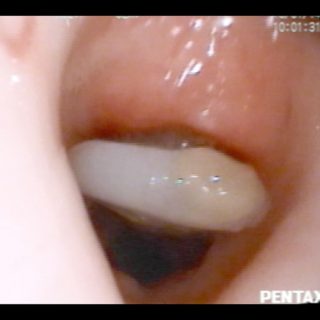
243 – Myofibroblastic Bronchial Tumor
“Threatening” aspect. With its reddish coloration that declares a sufficient vascularization, and its thick vessels that crown the visible hemisphere of this tumor that from the entrance of the right source bronchus, it challenges the bronchoscopist, tempting him to defer the biopsy to a safer time. A rigid bronchoscopy will make it possible to thermocoagulate … Read more